What additives can a lubricant contain?

What additives can a lubricant contain?
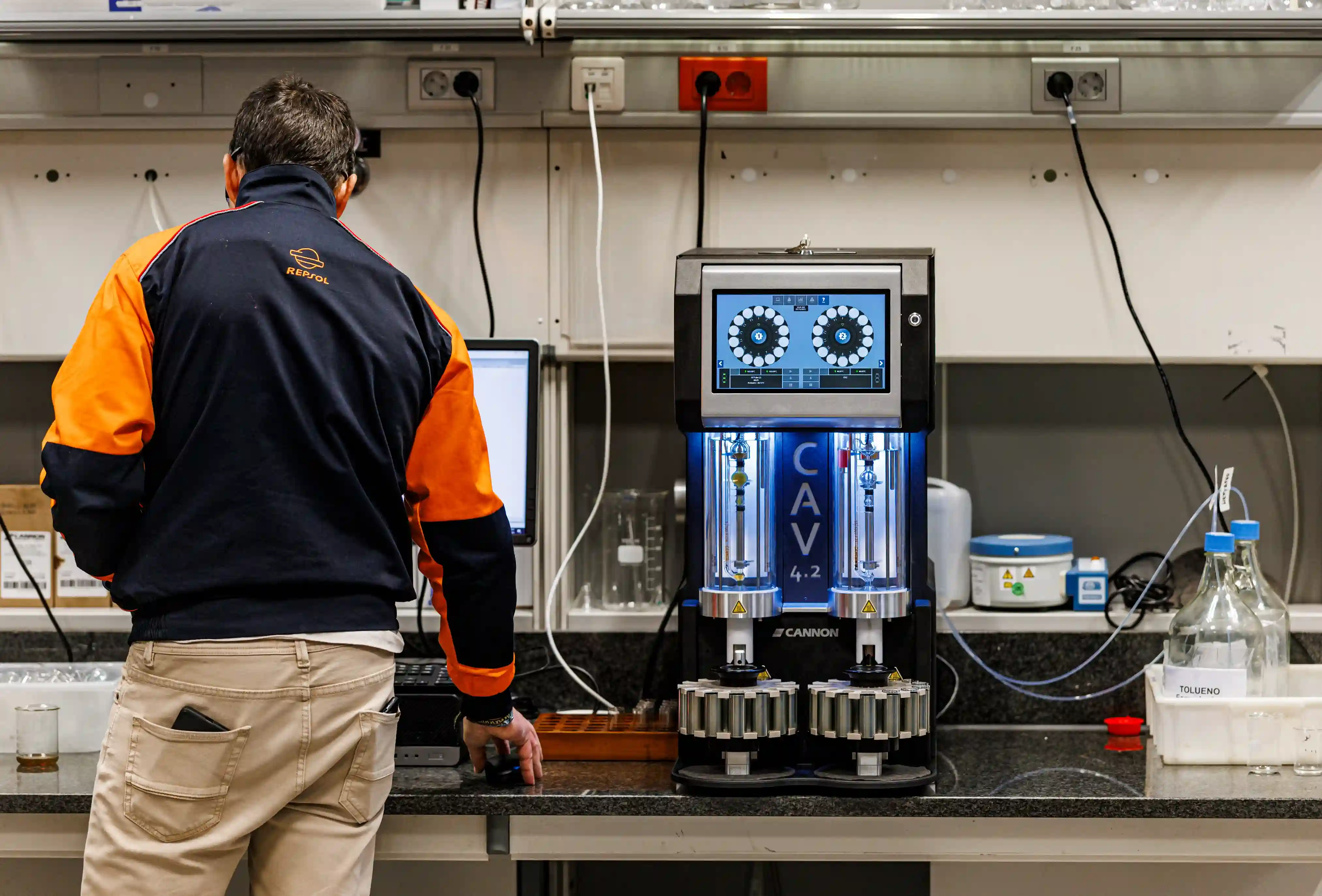
Technological developments in the world of automotive and industrial engines have led to an improvement in all the elements that go with them. Innovation and being at the forefront are the essence of Repsol’s work and, thanks to its Technical Support and Development team and its laboratories, such as the Repsol Technology Lab, it has succeeded in obtaining the best products and always being in first place in this constantly evolving technological era.
Lubricants are essential elements of engines, whether to ensure smooth running, performance, protection, or other features, and these are achieved by using additives.
The additives in lubricants are chemicals that are added to the “lubricant base” to improve its performance and properties, and/or to add new ones to perfect it.
Additives have three basic functions:
1. To improve the properties of the oil by adding elements that combat corrosion, wear, the build-up of deposits, etc.
2. To remove the properties that prevent the oil from giving the best performance.
3. To add elements that perfect its use and performance, and increasingly cover all the engine’s needs.
What classes of lubricant additives are there and what functions do they have?
- To get the best possible performance from lubricants, the additives must meet a series of objectives, including:
- Protecting the lubricant, preventing the oil rom oxidizing during the chemical changes that can occur during use.
- Slowing down wear in the machinery and the agents that can degrade it.
- Improving the properties of the lubricant, such as its fluidity.
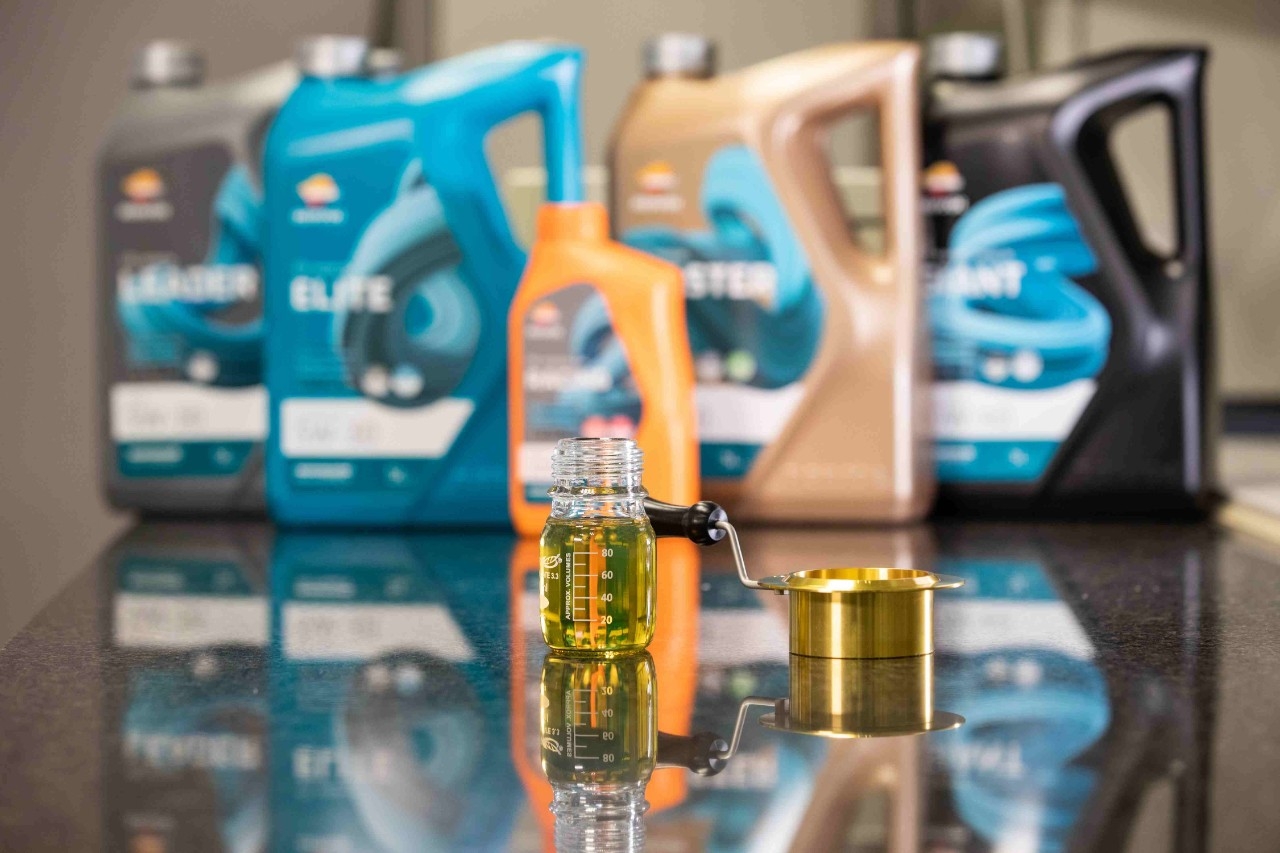
There are many classes of additives for lubricants, of which the following are the major ones:
Additives that improve the properties of the lubricant:
- Antioxidant additives: Their function consists of slowing down the oxidation that occurs as the lubricant ages and as a result of wear in the engine.
- Anti-corrosive additives: Corrosion occurs when the lubricant film that is in contact with the metal of the engine is not optimal and condensed water passes through it, oxidizing the metal walls. This additive strengthens the film between the lubricant and the metal, preventing corrosion.
- Anti-foam additives: This type of additive prevents the formation of foam in the oil due to oxygenation, preventing air bubbles from forming in the lubricating system.
- Antifreeze: This additive ensures that the lubricant flows easily when it is at low temperatures. It lowers the turning point.
- Viscosity index improver additives: These are used to obtain the correct viscosity at high and low temperatures.
Additives that create new properties in the lubricants:
- Detergent additives: These prevent the formation of layers and deposits in the essential parts of the engine
- Dispersant additives: These keep impurities suspended, preventing particles from accumulating until they are expelled by the filters or crankcase.
- Anti-wear additives: These create a film that protects the metal walls, preventing friction between them and the resulting wear.
- Thickeners: These form a more solid layer that retains the lubricant to obtain the right viscosity at high and low temperatures.
What are the best additives for engine lubricants?
There are numerous types of lubricating oils, each with different features because of the additives they contain. However, in general there is no perfect one as each engine possesses its own special features and this leads to their being a special, specific additive for each situation and case.
In general terms, the most important factor is that the lubricant itself has all the quality certificates since they are a guarantee that the additives meet the specifications and its quality.
Therefore, the most important criterion is to determine the specific needs of an engine or gearbox, to understand which additive is necessary, and to ensure that the lubricant used is of the highest quality possible.
Related contents